Taphorn, K., Mechlem, K., Sellerer, T., De Marco, F., Viermetz, M., Pfeiffer, F., Pfeiffer, D., & Herzen, J. Direct Differentiation of Pathological Changes in the Human Lung Parenchyma With Grating-Based Spectral X-ray Dark-Field Radiography. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 40(6), 1568–1578 (2021). 10.1109/TMI.2021.3061253
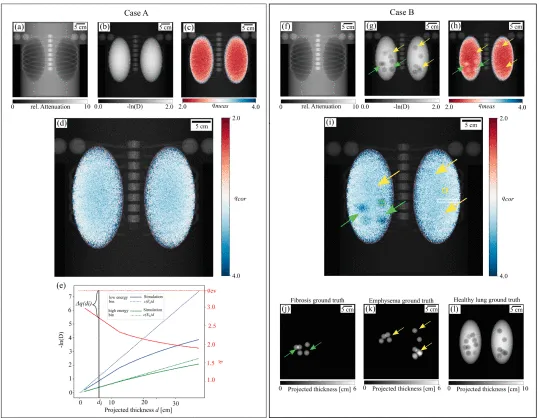
Purpose: we demonstrate the potential diagnostic power of grating-based X-ray dark-field in combination with spectral imaging in human chest radiography for the direct differentiation of lung diseases. We investigated the energy-dependent linear diffusion coefficient of simulated lung tissue with different diseases in wave-propagation simulations and validated the results with analytical calculations. Additionally, we modeled spectral X-ray dark-field chest radiography scans to exploit these differences in energy-dependency. The results demonstrate the potential to directly differentiate structural changes in the human lung. Consequently, grating-based spectral X-ray dark-field imaging potentially contributes to the differential diagnosis of structural lung diseases at a clinically relevant dose level.
Figure: Spectral X-ray dark-field radiography for two simulated cases